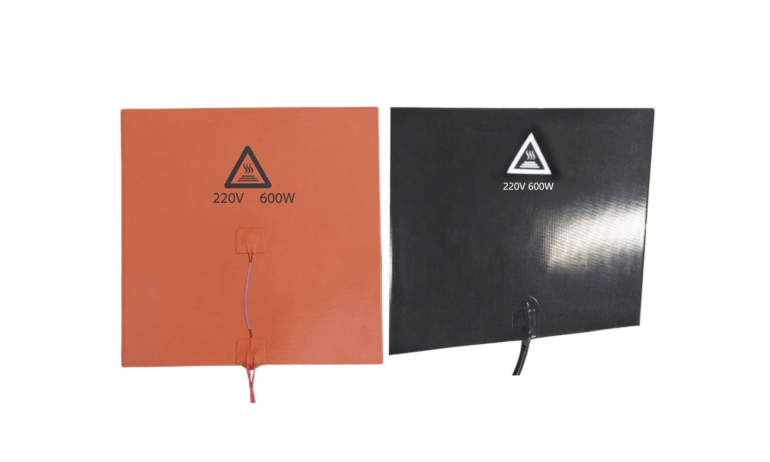

Does Your 3D Printer Need a Custom-Color Silicone Heater?
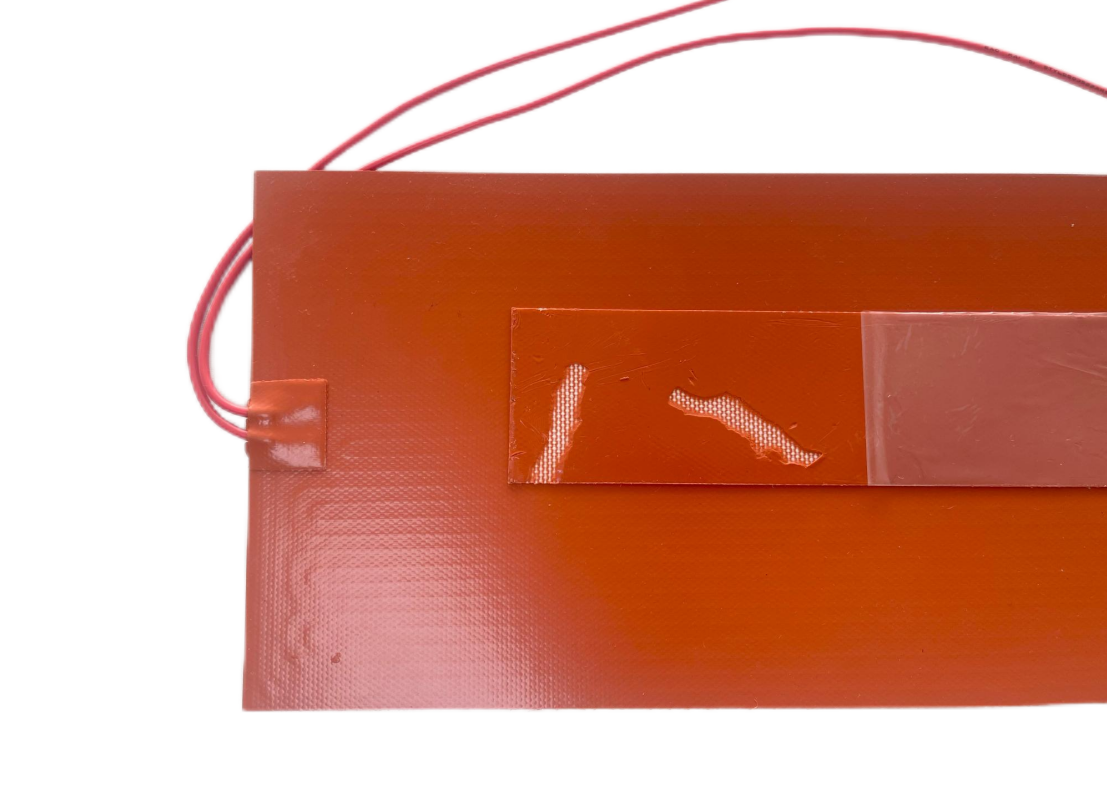

Do the Silicone Materials in Our Silicone Heaters Contain Fibers?

Understanding ITO Heater Thickness Impact on Resistance and Transparency
Transparent Heaters: Types, Sizes, Parameters, and Applications
Polyimide Heater with PT100 Sensor for Precision Thermal Management
Heaters are vital components in many industrial and consumer applications, used to generate heat for specific environments or materials. In some cases, heater elements (also known as heating elements or heat films) need to be connected in series, depending on the specific application requirements and system design. This blog explores the principles of series circuit design for heater elements, discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using a series connection, and reviews the appropriate scenarios for its use.
When heater elements are connected in series, the same current flows through each heating element, but the total supply voltage is divided across all the connected elements. This means that while the current remains constant, the voltage across each individual heater is a fraction of the total supplied voltage. Each heater element contributes to the overall power output of the system, and the performance of the series circuit is influenced by the electrical properties of each heater.
Several factors may determine whether a series connection is appropriate:
1. Voltage Matching:
In systems where the supply voltage is high, a single heater element may not be able to handle the entire voltage. By connecting multiple heaters in series, the voltage can be distributed among them, allowing for safer and more efficient operation.
2. Power Regulation:
A series connection allows engineers to control the total power output by varying the number of heater elements connected. This flexibility makes it easier to achieve the desired heating effect.
3. Safety Concerns:
In some applications, the failure of a single heater element can result in overheating or damage to the entire system. A series circuit mitigates this risk by breaking the circuit if any individual heater fails, preventing the remaining heaters from drawing excessive power and overheating.
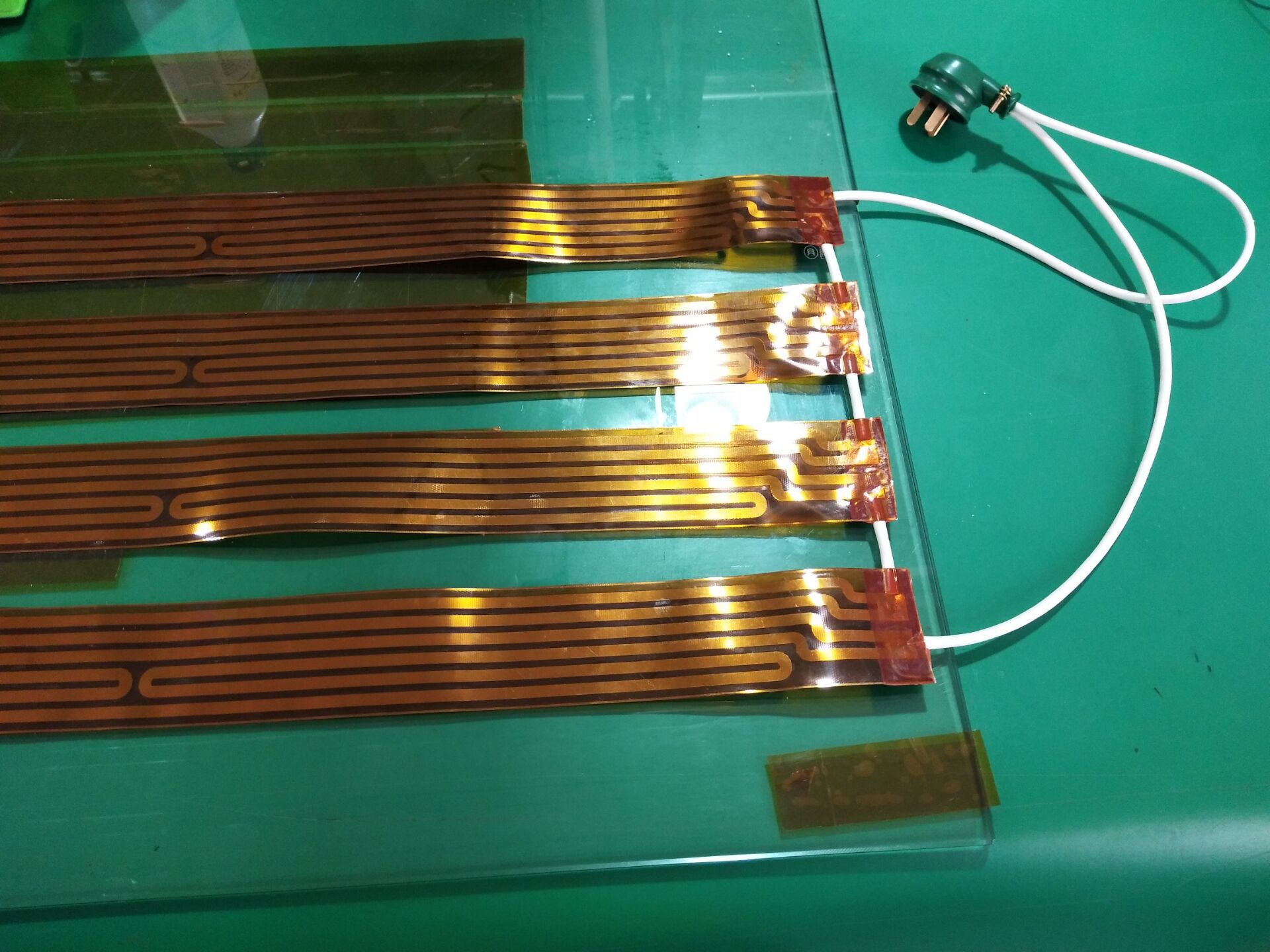
In a series configuration, the high supply voltage is split among the connected heaters, reducing the load on each individual element. This distribution helps each element operate within safe voltage limits, prolonging their lifespan.
2. Safety in Case of Failure:
If one heater in a series circuit fails, the entire circuit opens, which prevents the rest of the system from overheating. This can be a critical safety feature in systems where uncontrolled heating could lead to equipment damage or safety hazards.
3. Adjustable Power Output:
By adding or removing heaters from the series circuit, it is possible to easily adjust the total power output. This is especially useful in applications requiring precise control over the heating process.
One of the major drawbacks of a series configuration is its dependency on all elements functioning properly. If a single heater element fails, the entire circuit is broken, and the system will stop working until the faulty element is replaced.
2. Uneven Heating:
Small variations in the resistance of individual heaters can result in unequal power distribution, leading to uneven heating across the elements. This inconsistency can be problematic in applications that require uniform temperature control.
3. Design Complexity:
Designing a series circuit requires careful calculation of each heater's resistance and power consumption. Engineers must ensure the system remains balanced and stable, taking into account the electrical properties of each component.
It’s important to compare the series design with a parallel circuit, where each heater element is connected independently to the power supply.
Series Circuit:
Current remains the same, and voltage is divided among the heaters.
The circuit breaks if one heater fails.
Best for high-voltage, low-current applications.
Parallel Circuit:
Voltage remains the same, and current is divided among the heaters.
If one heater fails, the others continue to function.
Ideal for low-voltage, high-current applications.
A series connection of heater elements is an effective design choice for applications requiring voltage distribution, precise power control, and enhanced safety. However, it comes with trade-offs, such as system dependency on all heaters functioning properly and the possibility of uneven heating. Designers must carefully consider these factors when deciding whether a series configuration is appropriate for their specific application.
Understanding when and how to implement series circuits can greatly enhance the performance and reliability of heating systems across a variety of industries.

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.