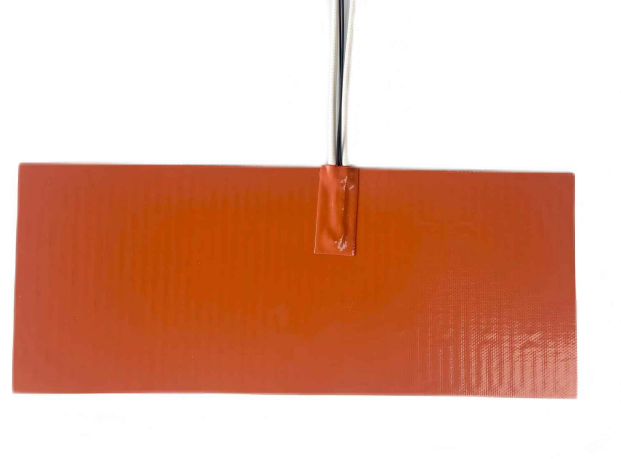

Why High-Temperature 3D Printers Need Rogers Silicone Heaters
Choosing the Right Thermostat for Smart Temperature Control Needs

Silicone Rubber Heaters in Automotive: Durability Meets Innovation

Polyimide Heaters: Key Applications in the New Energy Industry
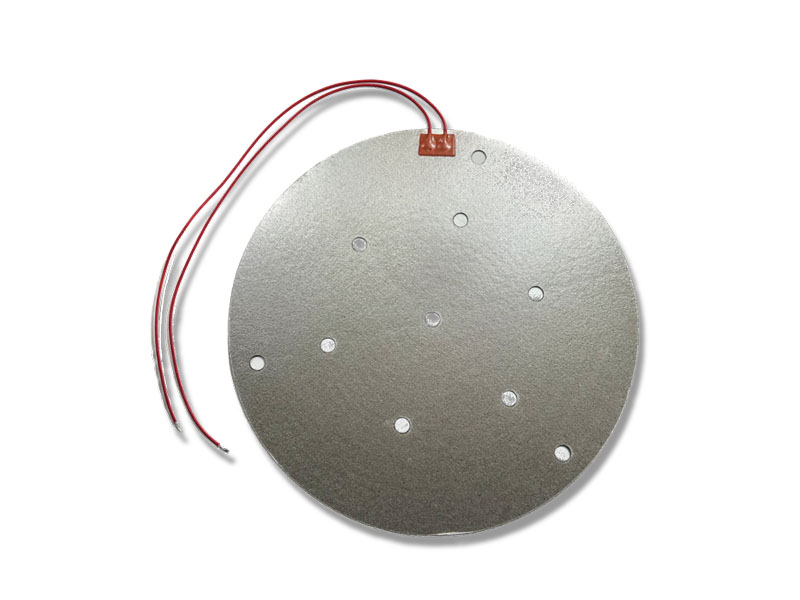

Why Mica Heater Need Multiple Through-Holes
Power density is a critical parameter in the design and application of flex heaters, influencing their performance, efficiency, and suitability for various applications. By understanding and calculating the power density, you can ensure your flex heater meets your specific heating requirements. This blog post will guide you through the process of calculating power density for flex heaters.
Power density is defined as the amount of power (in watts) delivered per unit area (in square inches or square centimeters) of the heater. It determines the intensity of heat output from the heater’s surface and plays a vital role in achieving the desired temperature and heating rate.
Temperature Control: Higher power densities result in higher temperatures, while lower power densities produce more moderate temperatures.
Application Suitability: Different applications require different power densities. For instance, industrial processes may need high power densities for rapid heating, whereas medical devices might need lower power densities for precise temperature control.
Energy Efficiency: Optimizing power density helps in achieving energy-efficient heating, reducing operational costs, and prolonging the heater's lifespan.
1. Determine the Heater’s Total Power (W)
The total power of the heater, usually specified in watts (W), can be found in the heater’s specifications or determined based on the power supply and heater design.
2. Measure the Heater’s Surface Area (A)
Measure the surface area of the heater in square inches (in²) or square centimeters (cm²). For rectangular heaters, multiply the length by the width. For irregular shapes, break the area into smaller, regular shapes, calculate their areas, and sum them up.
Formula for a rectangular heater: A=Length × Width
3. Calculate the Power Density (PD)
Divide the total power by the surface area to obtain the power density.
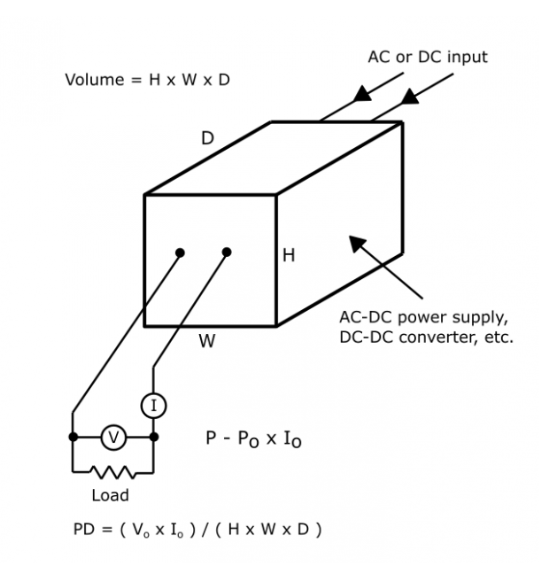
Formula: PD=P/A
l PD = Power Density (W/in² or W/cm²)
l P = Total Power (W) =Vo × Io
l A = Surface Area (in² or cm²)=H x W x D
Suppose you have a flex heater with a total power of 150 watts and a surface area of 10 square inches. Here’s how you would calculate the power density:
Total Power (P): 150 W
Surface Area (A): 10 in²
Power Density (PD):
PD=150W/10 in2=15 W/in2. Thus, the power density of the heater is 15 W/in².
Calculating the power density for flex heaters is essential for achieving efficient and effective heating. By understanding the heater’s total power and surface area, you can determine the power density and optimize it for your specific application. This ensures precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and the overall reliability of the heating system. If there is any question, please feel free to contact us at sales@hrx-heaters.com

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.