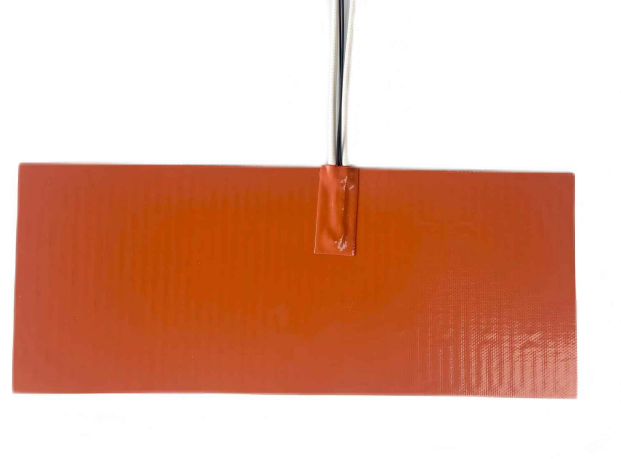

Why High-Temperature 3D Printers Need Rogers Silicone Heaters
Choosing the Right Thermostat for Smart Temperature Control Needs

Silicone Rubber Heaters in Automotive: Durability Meets Innovation

Polyimide Heaters: Key Applications in the New Energy Industry
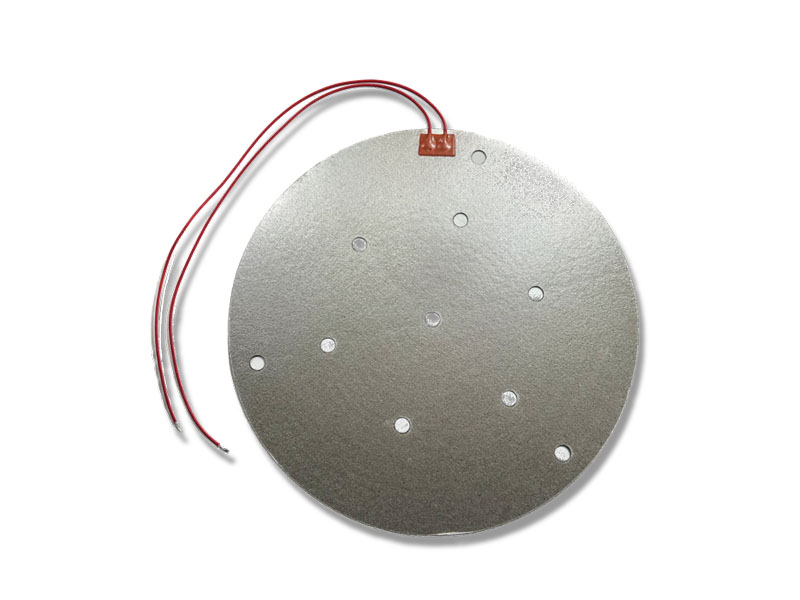

Why Mica Heater Need Multiple Through-Holes
In recent years, the rise of new energy power batteries has brought innovation and optimization across all components, including the heating elements used to manage temperatures in battery systems. A common setup involves affixing heaters to aluminum plates to efficiently regulate battery temperature. Interestingly, while Polyimide (PI) heaters have traditionally been favored for thermal applications, Epoxy Resin heaters are increasingly chosen for aluminum plate heating in power batteries. But why? This article explores the unique benefits of Epoxy Resin heaters for this application and compares them with Polyimide heaters.
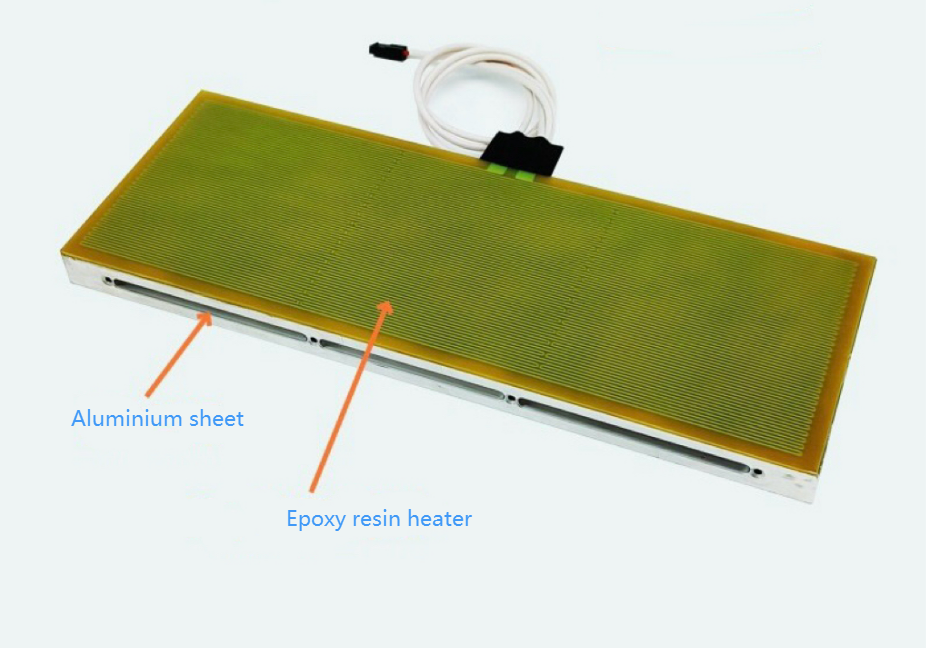
Epoxy Resin Heaters: Epoxy Resin heaters are known for their excellent adhesive properties, which allow them to firmly bond to aluminum plates. This strong adhesion is particularly beneficial in high-vibration or high-stress environments, where heaters may otherwise shift or detach. Epoxy’s mechanical stability ensures a robust bond, essential for the intense operating conditions often experienced by power batteries in electric vehicles and other high-demand applications.
Polyimide Heaters: PI heaters, while thin and flexible, generally lack the strong adhesive qualities of Epoxy Resin. PI heaters usually require an additional adhesive layer or bonding agent to attach securely to aluminum surfaces. This added complexity may reduce reliability in applications where frequent or intense vibrations occur.
Epoxy Resin Heaters: Epoxy Resin also offers impressive high-temperature resistance and excellent electrical insulation. These qualities make it a strong choice for power battery applications where temperature management and insulation are critical to performance and safety. Epoxy Resin heaters can withstand harsh environmental conditions, supporting consistent battery heating even during rapid temperature changes.
Polyimide Heaters: PI materials are known for their exceptional high-temperature range, typically functioning from -200°C up to 260°C. While PI heaters can also provide good insulation, their moisture resistance and durability in certain harsh conditions may not match the reliability of Epoxy Resin. This difference can impact long-term heater performance in power battery applications with fluctuating or extreme temperatures.
Epoxy Resin Heaters: Epoxy Resin heaters, when paired with aluminum plates, provide a relatively even distribution of heat. Although Epoxy itself is not as thermally conductive as aluminum, it complements the aluminum plate’s conductivity well, facilitating consistent heat transfer across the battery. This property is particularly advantageous in low-temperature environments, where effective, even heating is crucial for maintaining battery performance.
Polyimide Heaters: Polyimide has lower thermal conductivity, which can result in less uniform heating. For applications demanding consistent and stable temperature distribution, PI heaters might not achieve the same efficiency level as Epoxy Resin heaters when bonded to aluminum plates.
Epoxy Resin Heaters: One of the standout features of Epoxy Resin is its resistance to moisture and chemicals. For battery applications exposed to humidity or chemicals, Epoxy Resin heaters are highly suitable, as they can withstand challenging environments without degrading in quality. This durability is vital in applications where external conditions are unpredictable, ensuring reliable battery heating over time.
Polyimide Heaters: While PI heaters offer good corrosion resistance, they are not as effective as Epoxy Resin in highly humid environments. This limitation can affect PI heater performance in conditions where moisture control is critical, as in many power battery applications.
Epoxy Resin Heaters: Epoxy Resin heaters are generally more cost-effective than PI heaters and involve simpler manufacturing processes. This lower cost is appealing for large-scale production in new energy applications, making Epoxy Resin heaters a viable option for companies aiming to balance performance with budget constraints.
Polyimide Heaters: PI material, while high-performing, is typically more expensive, and processing it requires specific expertise. PI heaters are well-suited for high-precision applications, but in large-scale production, the costs can quickly accumulate. For power battery applications that do not require the ultra-high temperature tolerance of PI, Epoxy Resin provides a cost-effective alternative.
In conclusion, the choice of heater for aluminum plates in new energy power batteries often comes down to balancing adhesion strength, environmental durability, and cost-effectiveness. Epoxy Resin heaters excel in these areas, providing strong adhesion, high insulation, reliable performance in harsh conditions, and lower production costs. These characteristics make Epoxy Resin heaters a strategic choice for heating aluminum plates in power batteries, supporting effective thermal management and long-term reliability.
While Polyimide heaters have their advantages, particularly in extreme high-temperature environments, their lower adhesive qualities and higher costs may limit their practicality for power battery applications. As new energy technologies evolve, Epoxy Resin heaters offer a versatile, robust, and economical solution for aluminum plate heating, helping ensure that power batteries can perform at their best in diverse environments.

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.