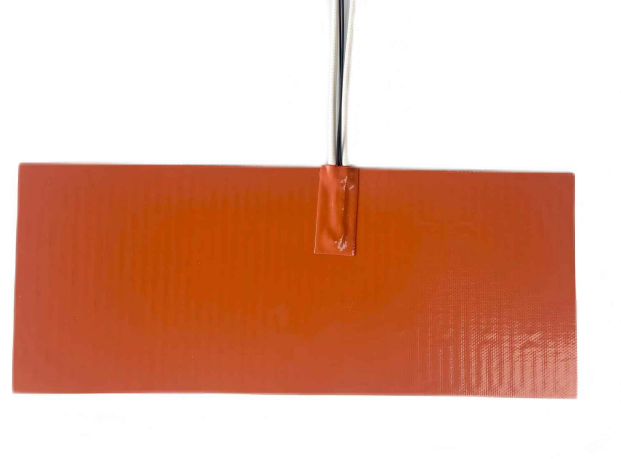

Why High-Temperature 3D Printers Need Rogers Silicone Heaters
Choosing the Right Thermostat for Smart Temperature Control Needs

Silicone Rubber Heaters in Automotive: Durability Meets Innovation

Polyimide Heaters: Key Applications in the New Energy Industry

Why Mica Heater Need Multiple Through-Holes
When it comes to flexible heating solutions, Polyimide heaters and Silicone heaters are two of the most widely used types. Each has its own unique properties and advantages, making them suitable for different applications. In this blog post, we will compare Polyimide heaters and Silicone heaters in terms of their material and construction, temperature range, thickness and flexibility, durability and environmental resistance, and weight. We will also provide guidance on choosing the right heater for your specific application.
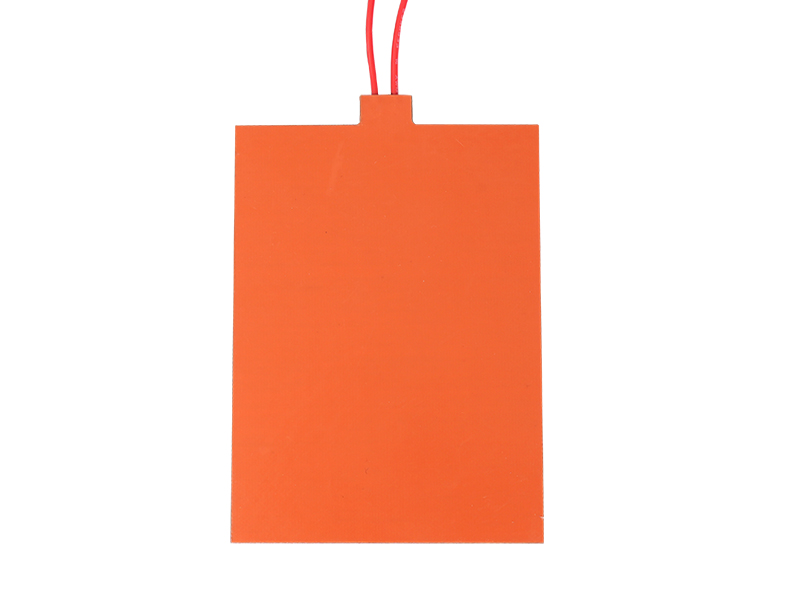
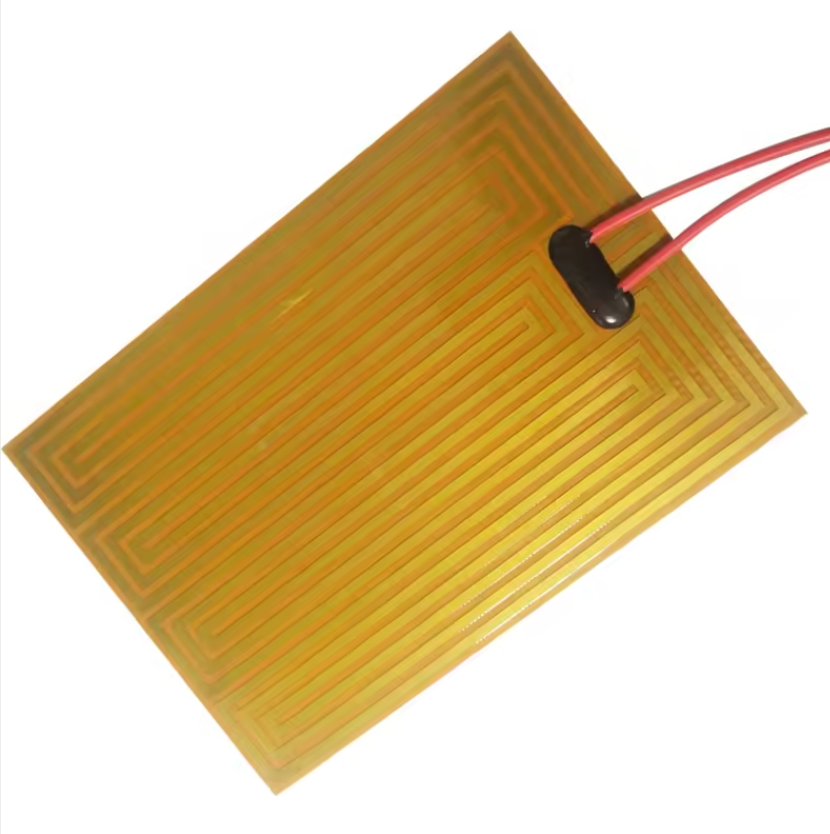

Polyimide Heaters: Polyimide heaters are made from polyimide film, a high-performance polymer known for its excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance. The heating element in Polyimide heaters is typically an etched foil, which is sandwiched between layers of polyimide film. This construction allows for extremely thin and flexible heaters.
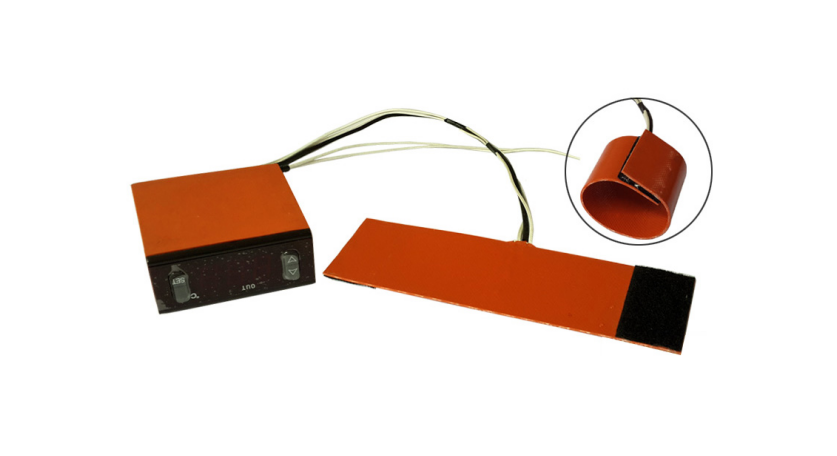
Silicone Heaters: Silicone heaters are made from silicone rubber, which is known for its durability and flexibility. The heating element in Silicone heaters can be either a resistance wire or an etched foil, encapsulated in silicone rubber. This construction results in a thicker and more robust heater compared to Polyimide heaters.
Polyimide Heaters: Polyimide heaters can operate in a wide temperature range, from extremely low temperatures down to -269°C (-452°F) and up to 200°C (392°F). This makes them suitable for applications requiring precise temperature control in both cryogenic and moderately high-temperature environments.
Silicone Heaters: Silicone heaters have a broader operating temperature range, from -60°C (-76°F) to 230°C (446°F). This makes them ideal for applications that require heating in more extreme environmental conditions, both hot and cold.
Polyimide Heaters: Polyimide heaters are known for being extremely thin, typically around 0.1mm to 0.3mm thick. Their thinness and high flexibility make them perfect for applications where space is limited and a lightweight solution is necessary. They can easily be integrated into compact and intricate designs.
Silicone Heaters: Silicone heaters are thicker, usually around 1.5mm to 3mm, but still offer good flexibility. Their thickness and robustness make them better suited for applications that require a durable heater capable of withstanding more rugged conditions.
Polyimide Heaters: While Polyimide heaters are less durable than Silicone heaters, they offer high resistance to chemicals and radiation. This makes them suitable for clean environments and applications where chemical exposure is a concern. However, they are not as resistant to mechanical damage as Silicone heaters.
Silicone Heaters: Silicone heaters are highly durable and robust, offering excellent resistance to mechanical damage, moisture, and harsh chemicals. This makes them ideal for industrial and outdoor applications where they may be exposed to tough environmental conditions.
Polyimide Heaters: Polyimide heaters are very lightweight, which is advantageous for applications where weight is a critical factor. Their lightness, combined with their thinness and flexibility, makes them ideal for precision applications in various fields.
Silicone Heaters: Silicone heaters are heavier than Polyimide heaters due to their thicker construction. However, their added weight is often a trade-off for the increased durability and robustness they provide.
Choose Polyimide Heaters if:
· You need a thin, lightweight, and flexible heating solution.
· Your application requires precise temperature control in tight spaces.
· You are working with electronics, aerospace, medical devices, or laboratory equipment.
· Chemical resistance and minimal outgassing are important factors.
Choose Silicone Heaters if:
· You require a durable and robust heater.
· Your application involves harsh environments, mechanical stress, or outdoor conditions.
· You are working with industrial equipment, automotive systems, or food service equipment.
· Durability, moisture resistance, and chemical resistance are key considerations.
Both Polyimide heaters and Silicone heaters offer unique advantages that make them suitable for different applications. By understanding the key differences between these two types of heaters, you can make an informed decision to select the one that best meets your specific needs. Whether you prioritize thinness and flexibility or durability and robustness, there is a flexible heating solution available to meet your requirements.

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.