
Vulcanization Bonding for High-Performance Silicone Rubber Heaters

How Aluminium Foil Heaters Work and Where to Use Them?

How PI Graphene Heating Films Achieve "Instant Heat-up" and "Ultra-Low Energy Consumption"?

12 Safety & Longevity Guidelines Before Installation for Flexible Film Heaters

Battery Drying & Formation Equipment Heating Plate
Polyimide heaters are widely used in various industries due to their excellent thermal properties and durability. One critical aspect of their design is the choice of conductor material. In this blog, we explore the differences in performance when using Stainless Steel and copper alloy (brass) conductors under the same conditions.
Experimental Setup
We conducted an experiment with a Polyimide heater of dimensions 500mmx500mm, powered by 220VAC and designed for a power output of 250W. The goal was to compare the performance of heaters using Stainless Steel and copper alloy conductors, starting from room temperature (25°C) and heating up to 130°C.
Material Characteristics
Stainless Steel (304):
Resistivity: Higher compared to copper alloys.
TCR: Lower, typically around 10 to 30 ppm/°C.
Copper Alloy (Brass):
Resistivity: Lower compared to Stainless Steel.
TCR: Higher, typically in the range of 100 to 200 ppm/°C.
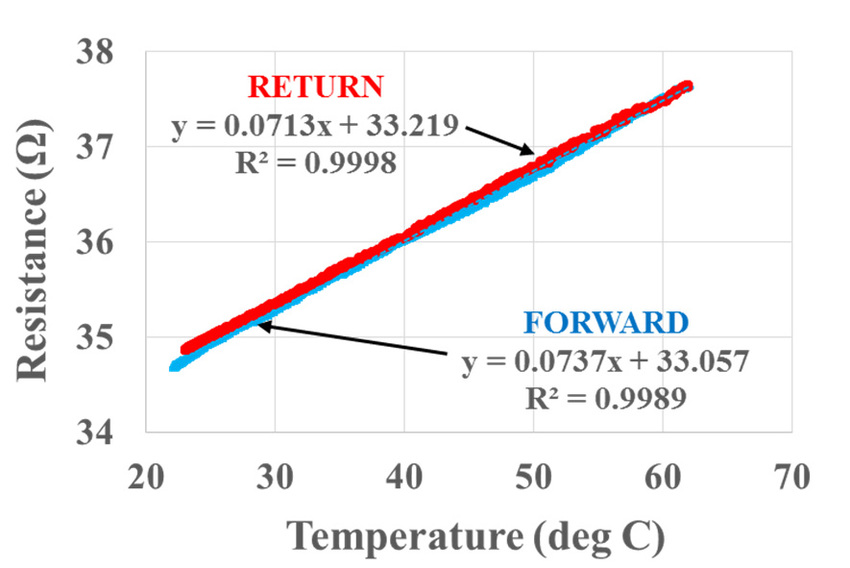
Experimental Results
Power Output: The heater with Stainless Steel conductors exhibited a higher power output at 130°C compared to the one with copper alloy conductors.
TCR: The copper alloy conductor showed a higher TCR, Polyimide heater TCR, meaning its resistance increased more significantly with temperature.
Analysis of Results
The observed results can be attributed to the following factors:
Initial Resistance: Stainless Steel has a higher initial resistance, but its TCR is lower, leading to a smaller increase in resistance as the temperature rises.
Resistance Increase: Copper alloy, with a higher TCR, experiences a more significant increase in resistance at higher temperatures, reducing its power output.
Impact on Usage
Heating Efficiency: Stainless Steel conductors may provide higher heating efficiency at higher temperatures due to lower resistance increase.
Temperature Stability: Copper alloy conductors, with a higher TCR in Polyimide heater, may lead to less temperature stability, which can be critical in applications requiring precise temperature control.
Power Stability: Stainless Steel conductors offer more stable power output, which is beneficial for consistent heating.
Practical Recommendations
Choose Stainless Steel: For applications requiring high temperature stability and power consistency, Stainless Steel conductors are preferable.
Choose Copper Alloy: For applications where initial heating speed and efficiency are prioritized, and some temperature fluctuation is acceptable, copper alloy conductors are suitable.
In summary, both copper alloy and stainless steel have their merits when used as conductors in Polyimide heaters. For customers prioritizing quick heat-up times and energy efficiency, copper alloy is the optimal choice. However, for applications requiring long-term stability and corrosion resistance, stainless steel offers significant advantages. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will guide you in choosing the right material for your Polyimide heater.

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.