
How Aluminium Foil Heaters Work and Where to Use Them?

How PI Graphene Heating Films Achieve "Instant Heat-up" and "Ultra-Low Energy Consumption"?

12 Safety & Longevity Guidelines Before Installation for Flexible Film Heaters

Battery Drying & Formation Equipment Heating Plate

How Flexible Heaters Achieve Consistent Medical Fluid Warming?
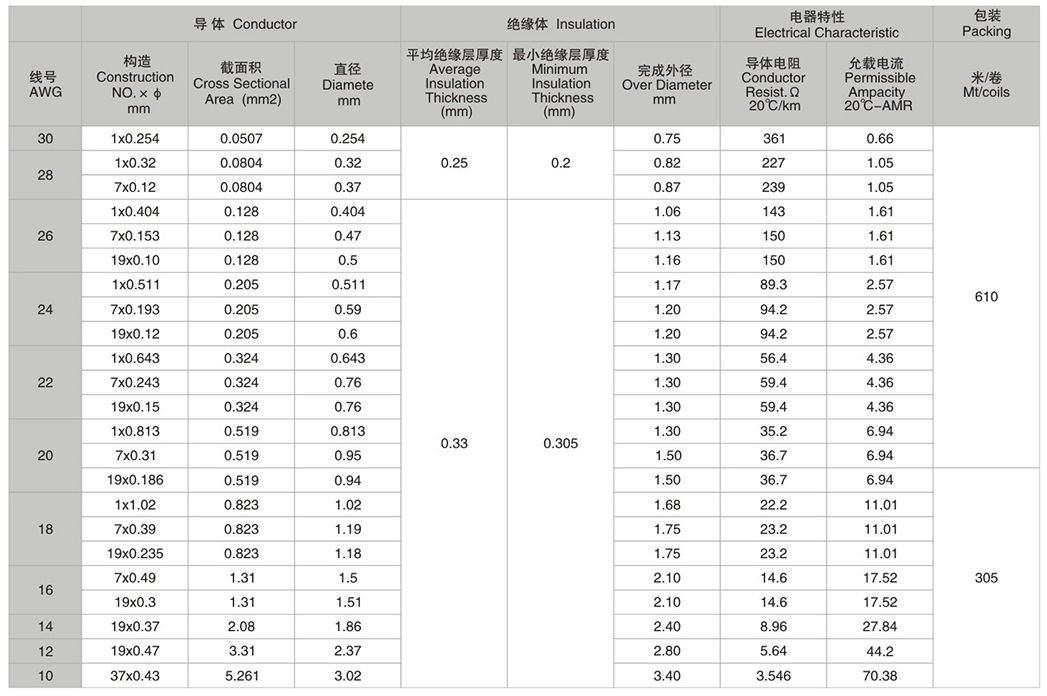
Selecting the correct wire gauge for electrical heaters is critical for ensuring both safety and efficiency. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system defines the diameter of the wire, which directly impacts its capacity to carry current without overheating or causing damage. In this article, we'll explore how to match the right wire for heaters, including calculating the current based on the heater’s specifications and choosing an appropriate wire gauge from the provided table.
Firstly, let's understand how to calculate the current required for a heater. The current ((I)) can be derived from the power ((P)) and voltage ((V)) of the heater using Ohm's Law: I=P/V
Let's use an example where the heater has a power rating of 250W at 230V: I=250W/230V≈1.09A. This means our heater draws approximately 1.09 amperes of current.
Step 2: Choosing the Correct Wire Gauge
With the current calculated, the next step is to find a wire gauge that can safely handle this amount of current. We refer to the provided table to identify suitable options.
From the table(refer to UL1332 FEP cable), we see that for a current of around 1.09A, the following wire gauges could potentially be used:
•AWG 26: Permissible Ampacity at 20°C - AMR is 1.61A, so AWG26 can comfortably accommodate the 1.09A current load.
Step 3: Selecting the Best Option
While AWG 26 meet the requirements, it is advisable to opt for a wire gauge that offers some additional headroom for future needs or unforeseen circumstances. When space permits, it is always safer to go one or two sizes larger than strictly necessary. So, considering the safety factor, AWG 24, which has a permissible ampacity of 2.57A, could also be considered.
Additional Considerations
•Wire Length: Longer wires may experience greater voltage drop and increased resistance. For extended lengths, consider upgrading to a thicker wire gauge.
•Operating Environment: High temperature environments or areas prone to physical strain should prompt the selection of a heavier gauge wire to prevent overheating and mechanical failure.
•Future Expansion: If there is a possibility of increasing the load in the future, opting for a larger wire gauge now can save costs and hassle later.
In summary, matching the right wire gauge to your heater involves understanding the current demand based on the heater’s power and voltage specifications. Using the provided table, you can easily identify suitable wire gauges. Always err on the side of caution by choosing a wire gauge that exceeds the minimum requirements, particularly if space constraints allow. This ensures not only compliance but also longevity and safety in your electrical installations.
If you have any specific questions or need further guidance on selecting the best wire gauge for your application, please don't hesitate to reach out.
Related product links

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.