
How Aluminium Foil Heaters Work and Where to Use Them?

How PI Graphene Heating Films Achieve "Instant Heat-up" and "Ultra-Low Energy Consumption"?

12 Safety & Longevity Guidelines Before Installation for Flexible Film Heaters

Battery Drying & Formation Equipment Heating Plate

How Flexible Heaters Achieve Consistent Medical Fluid Warming?
When customers order custom heaters, it is crucial to ensure that the heaters meet their specific temperature requirements. However, sometimes the initial specifications may not result in the desired temperature. In such cases, adjusting the voltage can help achieve the required temperature. This blog post will guide you through the process of adjusting voltage to test and re-customize heaters to meet customer requirements.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the adjustment process, it's important to understand the basic principles governing heater performance:
1. Power Calculation: The power ( P ) of a heater can be calculated using the formula:
P =V²/R where ( V ) is the voltage and ( R ) is the resistance.
2. Temperature Control: By adjusting the voltage, you can change the power output of the heater, which directly affects its temperature.
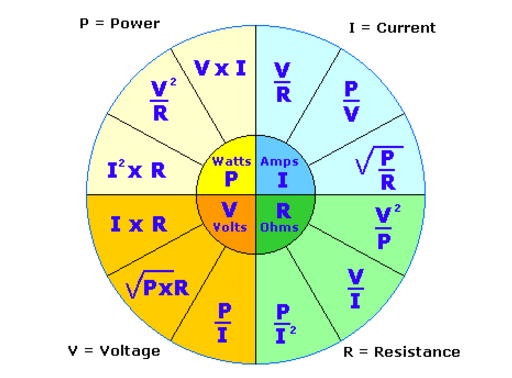
Case Study: Adjusting Voltage for a Custom Heater
Let's walk through a real-world example to illustrate the process.
Initial Specifications
• Voltage (( V_1 )): 24 V
• Power (( P_1 )): 50 W
• Resistance (( R )): 11.52 Ω
Step 1: Test the Initial Heater
1. Production: Produce the heater according to the initial specifications.
2. Testing: Test the heater to measure the actual temperature. Suppose the test shows that the temperature is not as expected.
Step 2: Adjust Voltage to Find Suitable Temperature
To find the suitable voltage, we can use the power formula to calculate the new power for different voltages and then test the heater.
1. Calculate New Power for Different Voltages:
• Example 1: Voltage ( V_2 = 36 ) V
P2 =(36V)²/11.52Ω
P2 =1296V²/11.52Ω
P2 ≈112.5W
• Example 2: Voltage ( V_3 = 30 ) V
P3 =(30V)²/11.52Ω
P3 =900V²/11.52Ω
P3 ≈78.125W
2. Test the Heater at Different Voltages:
• Test the heater at 36 V and record the temperature.
• If the temperature is too high, test the heater at 30 V and record the temperature.
• Continue testing at different voltages until you find the voltage that results in the desired temperature.
Step 3: Re-customize the Heater Based on Test Results
Once you have found the voltage that provides the desired temperature, you can either:
1. Continue Using the Adjusted Voltage: If the adjusted voltage meets the customer's requirements, you can continue using this voltage for the heater.
2. Re-customize the Heater: If the customer prefers a specific voltage (e.g., 24 V), you can re-customize the heater to match the new power requirement. For example, if the desired temperature is achieved at 30 V with 78.125 W, you can design a new heater with a resistance that matches this power at 24 V.
• Calculate New Resistance:
R new=V²desired/P test
R new=(24V)²/78.125W
R new=576V²/78.125W
R new≈7.37Ω
• Produce the New Heater: Manufacture the new heater with the calculated resistance.
Conclusion
Adjusting the voltage is a practical and effective method to ensure that custom heaters meet the required temperature specifications. By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you can test and re-customize heaters to satisfy customer needs. Whether you choose to continue using the adjusted voltage or re-customize the heater, the key is to systematically test and validate the performance to ensure optimal results.
We hope this guide helps you in your heater customization and testing processes. If you have any further questions or need assistance, feel free to reach out to us at sales@hrx-heaters.com
Related product links

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.