Both FPC and Polyimide Heaters use copper foil conductors and Polyimide insulation, making them seemingly similar at first glance. However, their differences in materials, structure, manufacturing processes, and applications reveal distinct functionalities tailored to different needs. This blog post explores these differences in detail.
FPC:
The conductor material used in FPC is limited to red copper, a high-purity copper foil. This choice ensures excellent electrical conductivity and reliability, critical for signal transmission in electronic devices.
Polyimide Heater:
In contrast, Polyimide Heaters offer a wide range of conductor materials depending on the desired heating temperature and resistance requirements. Options include Red Copper, Brass, White Copper, 304 Stainless Steel, Iron-Chromium-Aluminum, and Nickel-Chromium Alloy. The choice of material allows for customization to meet specific heating needs.
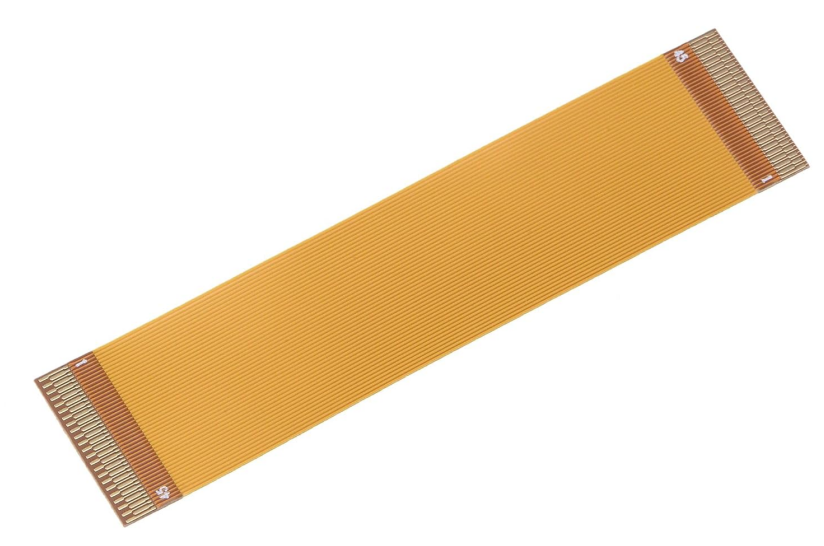 FPC
FPC
FPC:
FPC consists of a copper foil conductor layer sandwiched between one or more layers of Polyimide insulation. During manufacturing, the copper foil undergoes an etching process to create intricate circuit patterns. A protective Polyimide or other insulating material is then applied to ensure electrical stability and reliability. The primary focus here is achieving high-density circuit design for effective signal transmission in compact spaces.
Polyimide Heater:
Polyimide Heaters also utilize metal conductors (often copper foil or other high-resistance alloys) and Polyimide as the insulating layer. However, the manufacturing process focuses on forming heating circuits optimized for resistance and heat distribution. The conductor layer is typically thicker than in FPC to handle higher currents and generate the necessary heat efficiently.
FPC:
FPC is primarily used in electronic devices for circuit connections and signal transmission. Its flexible design allows circuits to be folded or bent, making it ideal for use in devices where space is at a premium, such as smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology.
Polyimide Heater:
Polyimide Heaters are designed for heating applications, generating heat through electrical current. They are commonly used in industries requiring precise temperature control, such as medical devices, aerospace, and industrial equipment. The focus is on even heat distribution and maintaining consistent temperatures.
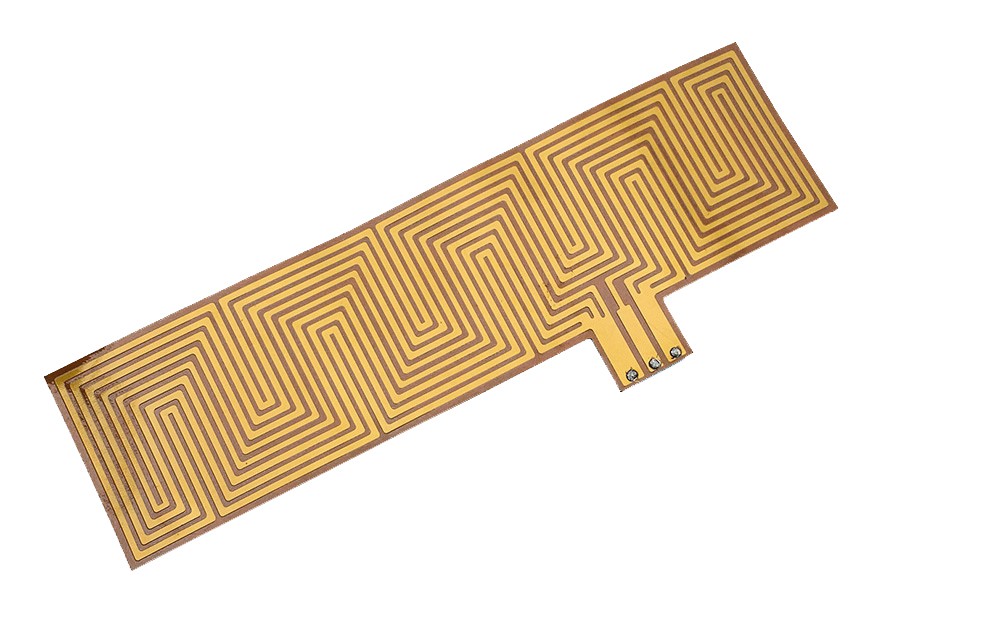 Polyimide heater
Polyimide heater
FPC:
Customers typically provide detailed designs (CAD/Gerber files) based on their functional needs. The circuit design can be complex, featuring varying line widths, impedance-controlled traces, and multi-layer circuits. The FPC manufacturer then produces the circuit based on these designs.
Polyimide Heater:
For Polyimide Heaters, customers generally need to specify basic parameters such as dimensions, voltage, power, and resistance. The heater manufacturer then designs the circuit, selecting appropriate conductor materials and ensuring that the heater meets the required specifications.
While FPCs and Polyimide Heaters share some similarities in materials, their differences are substantial, driven by their distinct applications and performance requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right technology for your specific needs, whether it’s for flexible circuit connections in compact electronic devices or precise heating solutions in specialized industries.

We offer a wide variety of high-efficiency heaters and heating element.Such as polyimide/kapton heaters,silicone rubber heaters,PET transparent heaters, thick film heaters,PTC heaters, mica heaters,epoxy resin heaters and graphene heating film.